Let’s be honest: juggling multiple tasks and deadlines can feel like herding cats.
Being a part of the project management teams over the years, I’ve worn many hats while managing different projects. Through trial and error (mostly error at first!), I’ve discovered a toolbox of project management techniques that have saved my sanity and countless projects.
So, in this blog, I’m sharing some of the best project management practices that can boost your organization, keep your team on the same page, and ensure projects land smoothly. We will see their usage techniques, the pros and cons, and even an expert tip for each.
Let’s get started!
What Are Project Management Techniques?
Project management techniques are systematic approaches used to efficiently organize, execute, and complete specific projects. These methods involve detailed planning, resource allocation, and execution strategies to ensure projects meet their objectives within designated timelines and budgets.
Effective project management typically includes setting clear goals, establishing timelines, defining responsibilities, and monitoring progress.
For example, structured project management methods can significantly enhance productivity and reduce costs in industries like construction or software development.
In fact, case studies from various sectors highlight that proper implementation of these techniques can lead to improvements in project completion times, demonstrating their critical role in order to achieve business outcomes.
Why Do You Need Project Management Techniques?

Project management techniques are crucial for several reasons, each contributing to the successful completion of projects across various industries.
Here are Some of the Reasons Why Project Management Techniques are Essential:
- Clarity and Direction: Project management provides a structured plan and clear objectives, helping everyone involved understand their tasks, the project goals, and the timeline. This ensures that all efforts are aligned and focused on achieving the desired outcomes.
- Resource Management: Effective project management ensures that resources, including time, budget, and manpower, are used efficiently. It helps in planning resource allocation so that the project can be completed within the allocated budget and timeline, minimizing wastage.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential risks and preparing strategies to mitigate them is a core component of project management. This proactive approach helps in avoiding surprises and managing possible impacts on the project schedule and outcomes.
- Problem Solving: Projects often face challenges and obstacles. Project management provides the tools and frameworks to address these issues systematically and efficiently, minimizing their impact on the project’s progress.
- Quality Control: Through consistent monitoring and evaluation, project management ensures that the project outputs meet the required standards and stakeholders’ expectations. This is crucial for the project’s success and the organization’s reputation.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Effective communication and stakeholder engagement are facilitated by good project management practices. Keeping everyone informed and involved helps in managing expectations and fostering a collaborative working environment.
- Adaptability: Project management frameworks like Agile emphasize adaptability and responsiveness to change. This is particularly important in dynamic environments where requirements, scope, and external conditions can change rapidly.
- Accountability: Clear roles and responsibilities are defined within project management, which enhances accountability among team members. This clarity helps in tracking progress and addressing any lapses in responsibility or performance.
- Improved Decision-Making: With structured methods for monitoring progress and performance, project management enables better decision-making. Data-driven insights help in making informed adjustments and improvements throughout the project lifecycle.
- Successful Delivery: Ultimately, the goal of project management is to deliver the project on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. Effective project management increases the likelihood of achieving this goal, leading to the overall success of the project.
So, project management techniques are indispensable tools for navigating the complexities of any project, ensuring efficiency, reducing risks, and enhancing the likelihood of success.
Read More: Common Project Management Challenges & How to Address Them
12 Best Project Management Techniques to Use in 2024
1. Agile Methodology
Agile Methodology is a dynamic project management and software development approach that helps teams adapt to changing requirements and deliver value faster. It emphasizes customer collaboration, flexible response to change, and iterative progress through small, fast cycles.
How to Use it:
- Divide the project into manageable units that can be completed in short cycles or sprints.
- Engage in continuous planning, testing, and integration throughout the project lifecycle.
- Encourage daily collaboration among all team members and stakeholders.
- Remain open and responsive to changes in project requirements at any stage.
- Regularly review and adapt the project direction based on feedback and results.
What You Will Like:
- Ensures high quality of the final product through regular testing and revisions.
- Increases control over the project with frequent reviews and adaptations.
- Boosts customer satisfaction by continuously involving them and accommodating changes.
- Provides more relevant and immediate metrics for assessing project performance.
- Enhances predictability and reduces risks by early identification and resolution of issues.
What You May Not Like:
- This can lead to unpredictable budgets and timelines due to ongoing changes.
- It may become inefficient if stakeholders frequently change their requirements.
Pro Tip: Use a culture of open communication and regular feedback among all team members and stakeholders. This cultural foundation can significantly enhance responsiveness and adaptability, which are critical for Agile success.
Read More: Agile Planning: What Is, Its Characteristics, & How It Works
2. Scrum
Scrum is an Agile framework that facilitates quick and efficient collaboration among team members working on complex projects. It structures development in cycles of work called sprints, allowing teams to adjust swiftly to changing requirements with minimal disruption.
How to Use it:
- Assemble your team and assign roles such as Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team.
- Plan and execute work in fixed-duration cycles known as sprints, usually lasting two to four weeks.
- Conduct daily stand-up meetings to assess progress and address any impediments.
- Review completed work with stakeholders at the end of each sprint and refine plans for upcoming sprints.
- Hold a retrospective meeting after each sprint to reflect on the process and make necessary adjustments.
What You Will Like:
- Encourages active and clear communication among team members.
- Quickly identifies and resolves issues, keeping projects on track.
- Prioritizes work based on the delivery of value to the customer.
- Adapts readily to changing project requirements without significant setbacks.
- Accelerates the delivery of usable products or features.
What You May Not Like:
- Demands a high level of commitment and experience from all team members to be effective.
- It may not be suitable for projects with large teams or where the project scope is continuously expanding.
Pro Tip: Regularly refine your backlog and prioritize it to ensure that your team is always working on the tasks that offer the most value to the project. This helps maintain focus and deliver results efficiently.
Read More: Read More: How to Create and Utilize a Scrum Board for Maximum Productivity
3. Kanban
Kanban is a visual project management approach that helps organizations enhance efficiency by visualizing their workflow processes. The Kanban system uses boards and cards to monitor progress and manage production processes in real time.
How to Use it:
- Create a visual representation of the workflow on a Kanban board with columns representing different process stages.
- Implement work-in-progress limits to avoid overloading team members and to identify bottlenecks.
- Continuously analyze the workflow and make adjustments to improve efficiency and throughput.
- Clearly define and make visible all process rules to ensure everyone understands workflow expectations.
- Regularly review and adjust the workflow and processes based on feedback and observations.
What You Will Like:
- Helps to minimize waste by managing and limiting current work-in-progress.
- Enhances the ability to deliver work faster and more consistently.
- Improves team focus and agility by making workflow steps visible and explicit.
- Facilitates ongoing improvements and efficiency in processes.
- Provides clear visibility into project progress and potential bottlenecks.
What You May Not Like:
- It can lead to a lack of attention to planning in favor of continuous delivery.
- It might oversimplify complex tasks, which can lead to issues in quality or execution.
Pro Tip: Regularly review and adjust your Kanban board’s layout and limits as your team’s efficiency and workload change. This dynamic adjustment helps maintain optimal flow and prevents bottlenecks.
Read More: Kanban Project Management: Everything you Need to Know
4. Lean Management
Lean Management is a systematic approach to streamlining both manufacturing and service processes by eliminating waste and optimizing efficiency. Originating from the Japanese automotive industry, it focuses on enhancing product value through customer-centric procedures.
How to Use it:
- Identify value from the customer’s perspective and focus all processes to enhance this value.
- Map out all steps in the value stream and eliminate any that do not contribute to customer value.
- Arrange for a seamless flow of materials and information through the process chain.
- Implement a pull system where production is based on customer demand to avoid overproduction.
- Strive for perfection by continuously seeking ways to reduce waste and improve processes.
What You Will Like:
- Significantly reduces waste, leading to cost savings and more efficient use of resources.
- Increases the speed and efficiency of production processes.
- Directly focuses on customer satisfaction by aligning production with customer needs.
- Promotes a company-wide culture of continuous improvement and efficiency.
- Helps to reduce inventory levels and space in production facilities, further lowering costs.
What You May Not Like:
- Implementation can be challenging as it requires comprehensive changes in company culture.
- Excessive focus on cost-cutting might compromise the quality or innovativeness of products.
Pro Tip: Implement “Kaizen” (continuous improvement) sessions to involve team members in identifying inefficiencies and suggesting improvements. This not only optimizes processes but also boosts team morale and engagement.
Read More: What Is Lean Project Management? It's Origin, Principles & Benefits
5. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects in any process, from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service. It uses statistical methods to improve quality by minimizing variability in business processes, thereby guaranteeing performance improvement.
How to Use it:
- Clearly define the project goals and customer deliverables.
- Measure the current process and its output to establish baselines for improvement.
- Analyze data to identify root causes of defects and opportunities for improvement.
- Improve the process by implementing solutions to address root causes.
- Control the new process to ensure consistent results and make continuous improvements.
What You Will Like:
- Provides a clear and quantifiable improvement in process quality and reliability.
- Delivers enhanced customer satisfaction by ensuring quality delivery.
- Helps in reducing operational costs by improving process efficiency.
- Employs robust analytical and statistical tools to identify and solve quality issues.
- Encourages better understanding of processes, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
What You May Not Like:
- Implementation can be complex and requires significant statistical knowledge.
- It may be perceived as inflexible, particularly in environments requiring high creativity and variability.
Pro Tip: Utilize statistical software and Six Sigma tools like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) rigorously to analyze processes and identify variations. This systematic approach can lead to more accurate insights and effective solutions.
Read More: Different Project Management Terms Beginners Should Know
6. Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model is a traditional project management method characterized by a sequential, linear process of project completion. It is often used in software development, where each phase must be completed before the next one begins, making it easy to understand and manage.
How to Use it:
- Thoroughly plan the entire project upfront and set clear, sequential phase objectives.
- Execute each project phase thoroughly before moving on to the next.
- Ensure thorough documentation at each stage to support project continuity and handovers.
- Review project progress at the end of each phase to ensure all objectives have been met before proceeding.
- Maintain strict adherence to the initial project plan, making adjustments only when absolutely necessary.
What You Will Like:
- Provides a clear, well-documented pathway from project start to finish.
- Helps to ensure all project requirements are considered upfront.
- Facilitates easy management and scheduling with clear milestones and deliverables.
- Suits projects with well-understood requirements that are unlikely to change.
- Supports rigorous documentation, which is beneficial for complex projects requiring detailed analysis.
What You May Not Like:
- Its inflexible structure makes it difficult to incorporate changes once the project is underway.
- High risk of project overruns if all requirements are not perfectly understood from the start.
Pro Tip: Ensure that you conduct thorough requirement analysis and planning phases. Since the Waterfall model depends heavily on the initial requirements and plan, having a detailed and accurate start is crucial for successful project execution.
Read More: A Guide to Waterfall Project Management Methodology
7. PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments)
PRINCE2 is a globally recognized project management methodology characterized by its defined processes and structured phases. It provides a detailed step-by-step approach for handling projects of all types and sizes, focusing on tight control and clear delivery frameworks.
How to Use it:
- Adapt the methodology to suit the project’s environment, size, complexity, importance, and team capability.
- Divide the project into manageable stages and plan, delegate, monitor, and control each one effectively.
- Regularly review project progress against the initial plan and the continuing business case.
- Manage any deviations from the plan rigorously, using defined governance arrangements.
- Engage with stakeholders and management at key project stages to ensure alignment and commitment.
What You Will Like:
- Delivers a systematic and structured approach that can be tailored to suit any project.
- Ensures clear definition of roles and responsibilities for team members.
- Provides strong control over project resources and stages, enhancing management capability.
- Supports effective decision-making through a focus on business justification.
- Widely recognized and understood, offering compatibility with other corporate practices.
What You May Not Like:
- It can be seen as overly bureaucratic, particularly in smaller projects.
- Requires significant training and understanding to implement effectively.
Pro Tip: Use the PRINCE2 principle of “managing by stages” to make complex projects more manageable by breaking them into smaller, controlled stages. This allows for easier monitoring and corrective actions without overwhelming the project team.
Read More: How to Become a Project Manager and Succeed in the Business World
8. Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method is a thorough project management technique focused on timely project completion. It involves identifying the longest stretch of dependent tasks and measuring the time required to complete them from start to finish, ensuring project milestones are met on time.
How to Use it:
- List all tasks necessary to complete the project and link them based on their dependencies.
- Draw a network diagram to visualize task sequences and identify the critical path.
- Calculate the earliest and latest start and finish times for all tasks to determine their float.
- Focus resources on critical tasks to prevent delays in the overall project timeline.
- Continuously monitor critical path tasks and adjust resources and schedules to maintain the path.
What You Will Like:
- Enhances understanding of essential tasks and their impact on the overall project timeline.
- Facilitates optimal allocation of resources to ensure project deadlines are met.
- Increases project transparency, helping stakeholders understand task dependencies and timelines.
- Useful for managing complex projects with many interdependent tasks.
- Helps avoid schedule conflicts and manage project delays effectively.
What You May Not Like:
- Setup and maintenance of the critical path can be complex and time-consuming.
- Less flexible in accommodating project changes, requiring updates across the entire plan.
Pro Tip: Regularly update and monitor your critical path. Since the critical path determines the project duration, any changes or delays in critical tasks can significantly impact the overall project timeline.
Read More: Everything You Need to Know About Critical Chain Project Management
9. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
PERT is a project management tool used to schedule, organize, and coordinate tasks within a project. It allows project managers to estimate the time required to complete a project by identifying the least amount of time needed to complete each task with an understanding of variability.
How to Use it:
- Define the scope and tasks of your project and gather estimates for the shortest, most likely, and longest times to complete each task.
- Construct a PERT chart that plots tasks as nodes and uses arrows to indicate the flow of the project.
- Calculate the critical path by determining the sequence of tasks that represent the longest path through the project.
- Adjust resources and timelines based on ongoing performance against the project estimates.
- Use the PERT analysis to identify and manage potential delays before they impact the critical path.
What You Will Like:
- Provides a comprehensive view of the project schedule and scope, accommodating uncertainty in task durations.
- Helps identify critical tasks that need more focus to ensure timely project completion.
- Encourages continuous monitoring and adjustment of timelines and resources.
- Particularly effective in planning and controlling large-scale and complex projects.
- Promotes proactive management of project risks and uncertainties.
What You May Not Like:
- Requires regular updates to reflect true project dynamics, which can be resource-intensive.
- Relies heavily on estimates, which can introduce errors if not accurately predicted.
Pro Tip: When using PERT, conduct regular risk assessments and update estimates as the project progresses. This helps maintain accurate projections and better prepare for potential delays.
Read More: 10 Charts & Diagrams for Better Project Management
10. Hybrid Techniques
Hybrid project management combines elements from various traditional and agile methodologies to create a flexible and tailored approach. This technique allows teams to leverage the strengths of structured and iterative practices to meet diverse project demands effectively.
How to Use it:
- Assess the project requirements to decide which methodologies to blend.
- Integrate structured phases for complex issues that require detailed planning and agile cycles for areas needing flexibility.
- Apply agile practices like scrums or sprints for tasks that benefit from fast iteration.
- Utilize traditional project management phases for parts of the project that require rigorous control.
- Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of the combined approach and adjust methodologies as needed.
What You Will Like:
- Offers flexibility to adapt to various project needs, providing a balanced approach.
- Combines the predictability of traditional methods with the adaptability of agile approaches.
- Allows for customization to address the specific challenges and strengths of the project team.
- Facilitates effective collaboration across different teams with varied expertise.
- Suitable for complex projects that require comprehensive management and rapid innovation.
What You May Not Like:
- Management of hybrid methods can be complex, requiring adept skill and experience.
- The mix of methodologies may lead to confusion and dilution of best practices without careful implementation.
Pro Tip: Clearly define when to use different methodologies within your hybrid approach to avoid confusion and overlap. Clear rules and conditions for switching methodologies can streamline project management and enhance team clarity.
Read More: The Hybrid Work Model and Why It Will Remain Relevant
11. Extreme Project Management (XPM)
Extreme Project Management is designed for projects characterized by a high degree of uncertainty or changing scopes. XPM prioritizes flexibility and rapid adaptation over rigid planning and control, making it suitable for innovative and high-impact projects.
How to Use it:
- Emphasize flexibility in project planning and execution to accommodate frequent changes.
- Implement iterative development processes to quickly respond to changes and updates.
- Maintain minimal project documentation to reduce overhead and increase responsiveness.
- Empower team members to make decisions quickly and autonomously.
- Engage in proactive risk management to anticipate and mitigate potential disruptions.
What You Will Like:
- Highly adaptable to rapidly changing project environments.
- Reduces time to market for new innovations significantly.
- Promotes a culture of innovation and flexibility in problem-solving.
- Ideal for projects with high uncertainty and risk where traditional methods may fail.
- Encourages strong team collaboration and empowerment.
What You May Not Like:
- This can lead to insufficient planning and oversight, potentially impacting project cohesion.
- High risk of scope creep as ongoing changes may lead to continuous expansion of project boundaries.
Pro Tip: Prioritize clear and concise communication to ensure that all team members remain aligned in a fast-paced, constantly changing environment. Regular, brief updates can prevent misalignment and confusion in extreme project scenarios.
Read More: AI in Project Management: A Complete Walkthrough
12. Digital Project Management Tools
Digital Project Management Tools encompass a range of software solutions designed to enhance project oversight and execution. These tools facilitate planning, tracking, and collaboration, making managing projects across different scales and complexities easier.
How to Use it:
- Choose a digital tool that aligns with the project’s scale and complexity.
- Set up project timelines, milestones, and deliverables within the tool.
- Utilize the tool’s collaboration features to keep team members connected and informed.
- Monitor project progress through the tool’s built-in analytics and reporting functions.
- Integrate other software tools and apps to extend functionality and streamline workflows.
What You Will Like:
- Improves organizational efficiency and project visibility across all stages.
- Enables seamless communication and collaboration, which is essential for geographically dispersed teams.
- Scalable and adaptable to a wide range of project sizes and types.
- Provides instant updates and alerts to keep all stakeholders informed.
- Automates and streamlines administrative tasks, reducing manual errors and saving time.
What You May Not Like:
- This may involve significant costs, especially for high-end enterprise solutions.
- Often requires training and acclimation for team members, which can be time-consuming.
Pro Tip: Take full advantage of your digital tools’ integrative capabilities. Integrating your project management software with other tools (like email, calendar, and coding repositories) can greatly enhance efficiency and keep all information centralized and accessible.
Elevate Your Project Success With Top Management Techniques & Tools
Effective project management techniques are indispensable for steering projects toward success and optimizing team performance. You can use proven methods & techniques to enhance your ability to manage timelines, resources, and team collaboration, ensuring that projects are delivered efficiently and meet their intended goals.
If you are looking for the most effective project management tool, I suggest you use the ProProfs Project software. It has an intuitive user interface, real-time collaboration features, and versatile reporting capabilities. Its seamless integration with other tools enhances its utility, ensuring effective usage of project management techniques for outstanding project outcomes.
Learn More About Project Management Techniques
What are the 4Cs of Agile?
The 4Cs of Agile are Collaboration, Creativity, Communication, and Change. Collaboration emphasizes teamwork and active involvement among all stakeholders. Creativity encourages innovative approaches to solving problems and developing products. Communication involves clear, transparent, and continuous exchanges among team members to ensure alignment and shared understanding. The change recognizes the dynamic nature of project requirements and the need to adapt processes and products responsively.
What are the four levels of project success?
The four levels of project success are project efficiency, impact on customers, business success, and preparing for the future. Project efficiency relates to meeting the initial time, budget, and quality specifications. Impact on customer evaluates how well the project outcomes meet or exceed customer expectations. Business success assesses the project’s contribution to the organization’s performance and goals. Preparing for the future considers the project’s role in positioning the organization for future opportunities and challenges.
Read More: SWOT Analysis | A Way to Boost Project Success Rate
What is Level 4 project management?
Level 4 project management refers to a maturity stage where processes are quantitatively managed. At this level, organizations use metrics and detailed analysis to measure project performance and quality, aiming for predictable processes that can be optimized further. It involves systematic data collection, statistical analysis, and quantitative techniques to understand and control variations in project execution. This level helps in achieving consistent project outcomes and continuous improvement.
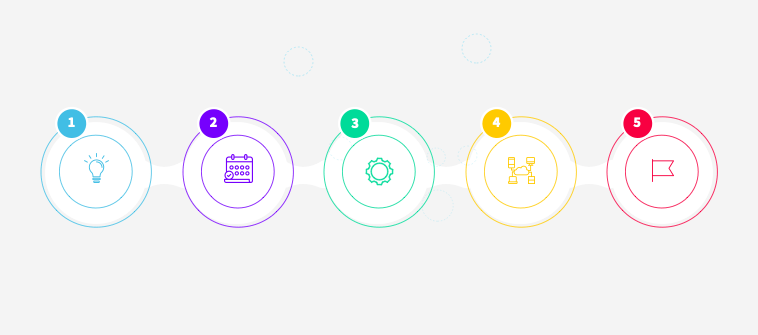
What are the 5 steps in project management?
The five steps in project management are initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. In the initiation phase, the project’s viability and objectives are established. Planning involves setting the roadmap, resources, timelines, and budgets. Execution sees the implementation of the plan. Monitoring and controlling involves tracking the project’s progress and making necessary adjustments. Closure finalizes all activities, delivers the project output, and reflects on lessons learned.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!